<Nicely seperated strands>
1. Helicase
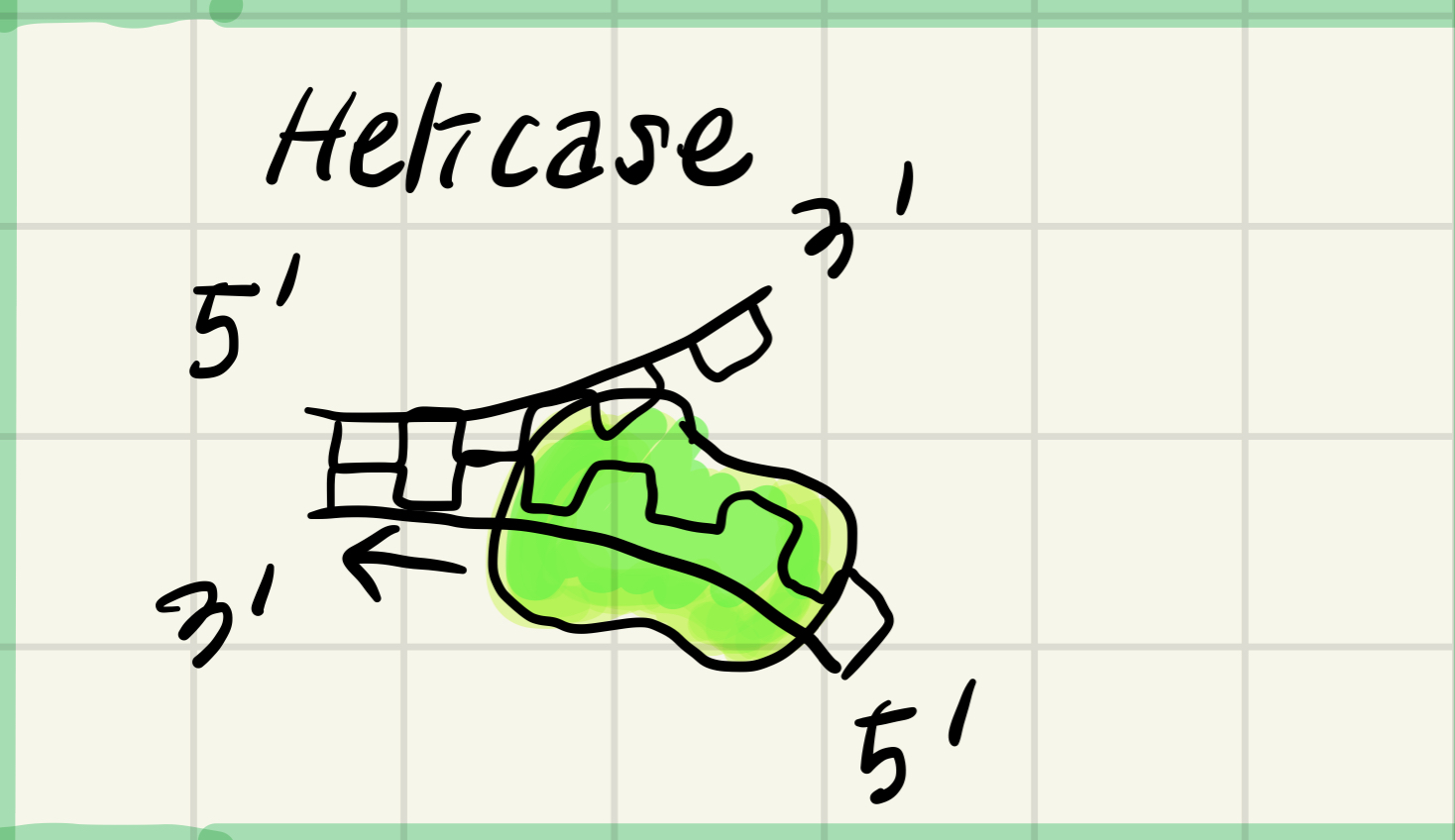
Unwind parental double helix at replicaction forks
open up the couble helix
2. Single-strand binding
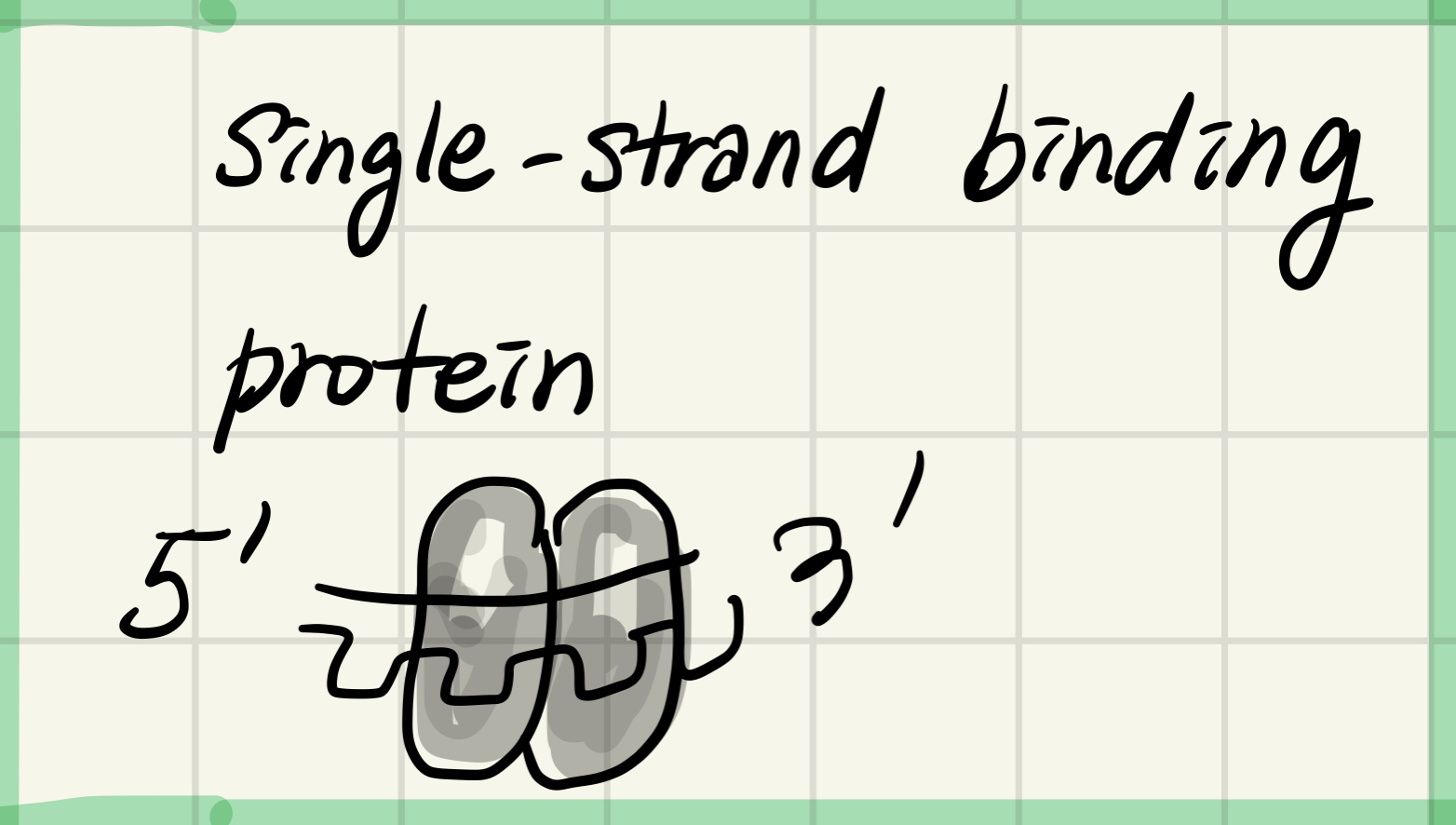
Binds to and stabilizes(안정시키다) single-stranded DNA until it is used as a template
Bind to unpairing strand and keeps them from rebinding with other strand again.
3. Topoisomerase
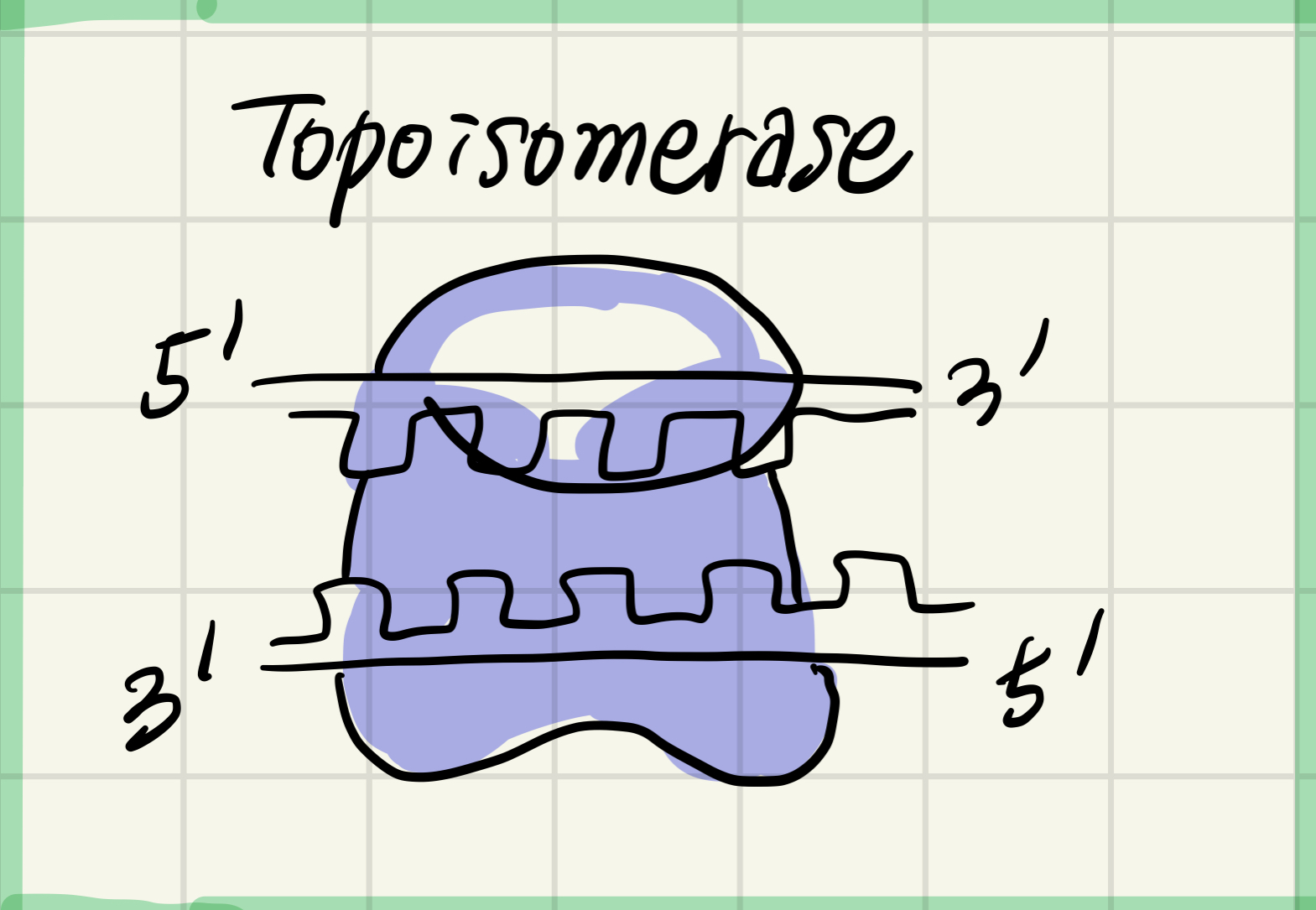
Relieves overwinding strain ahead of replication forks by breaking, swiveling, and rejoining DNA strands
Protein relieves(완화, 정리) the strand
4. Primase
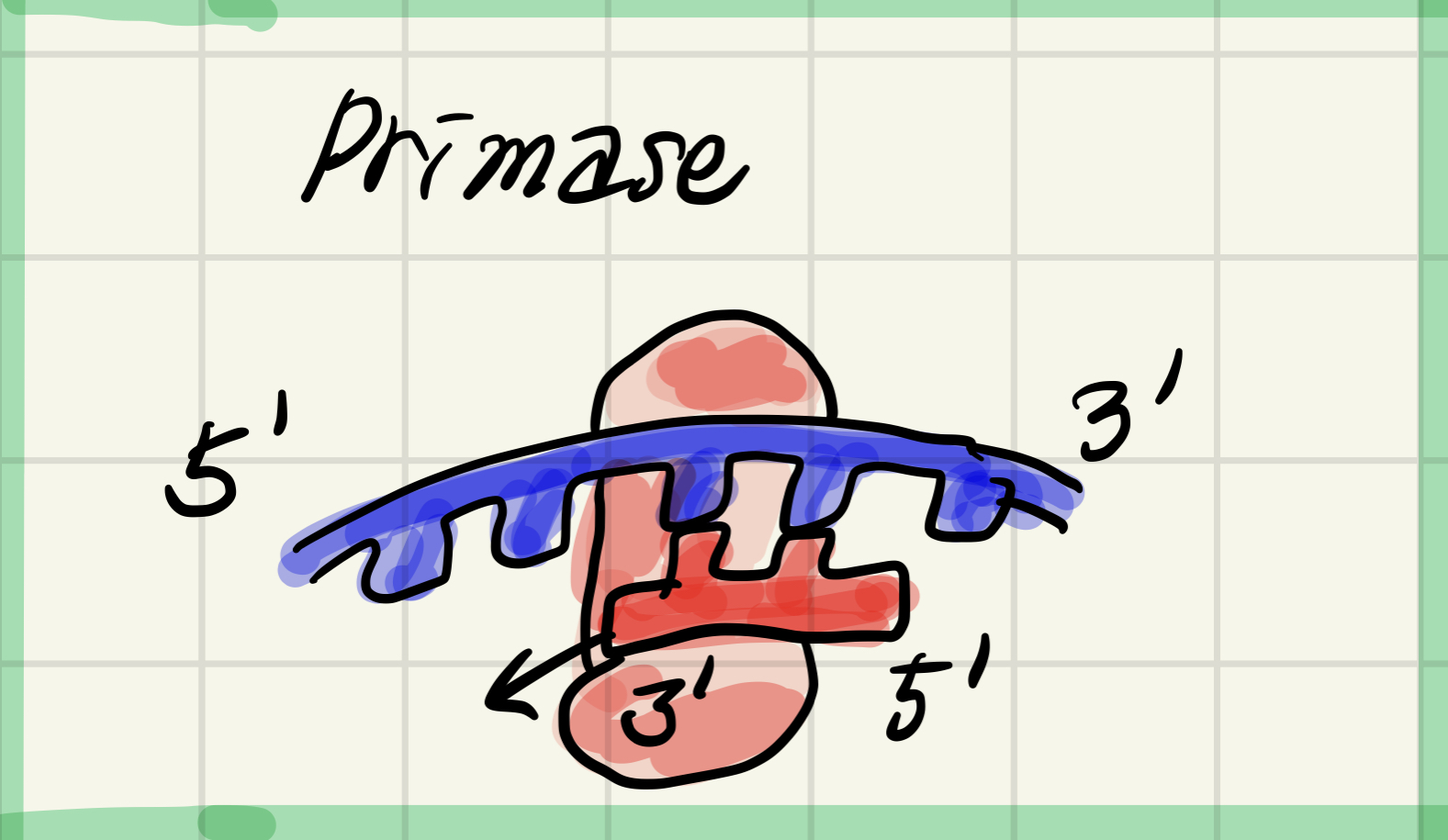
Synthesizes an RNA primer at 5' end of leading strand and at 5' of each okazaki fragment(파편) of lagging strand.
Synthesizes a short RNA primer (5-10nt).
*nt = nucleotide
5. DNA polymerase 3 (DNA pol 3)
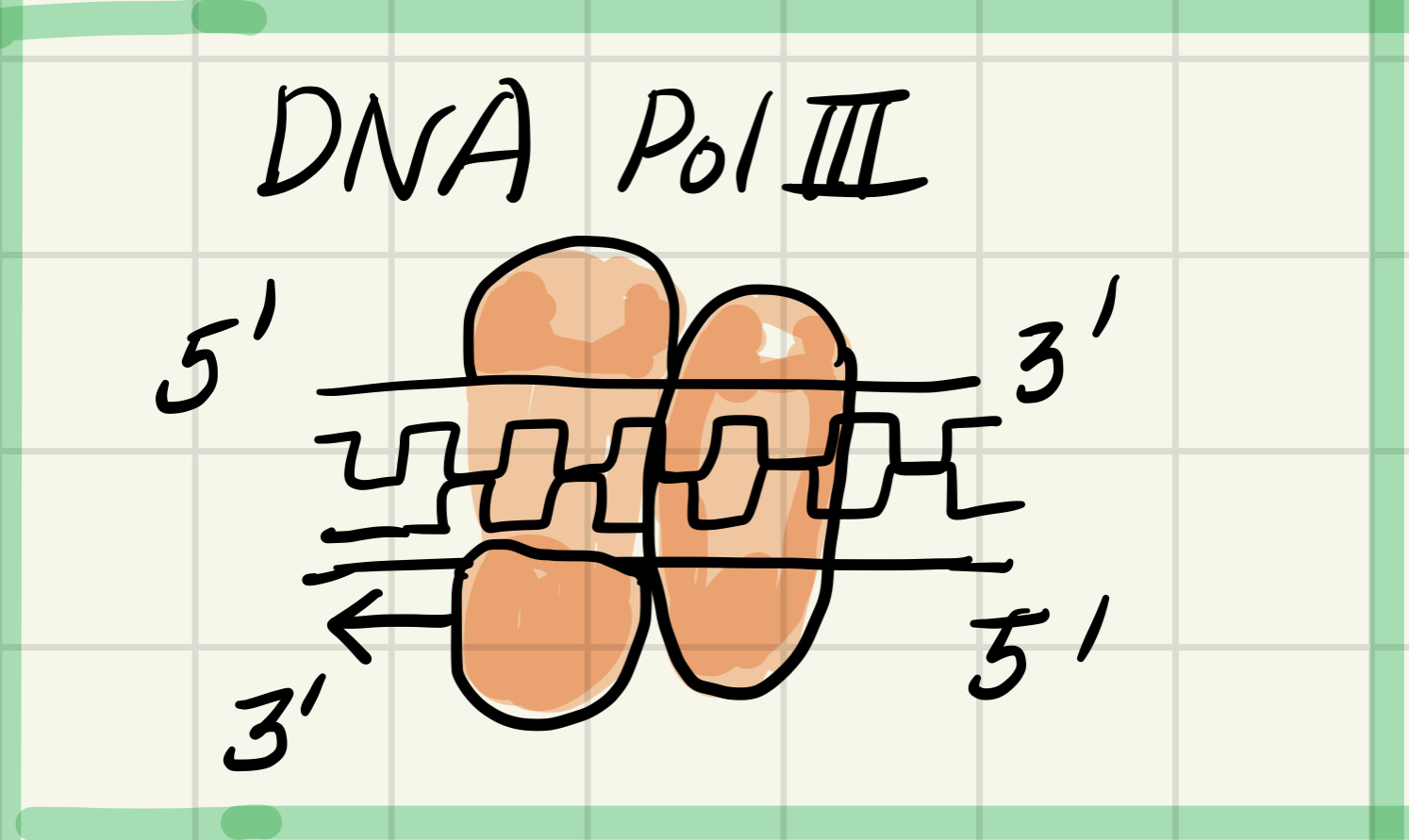
Using parental DNA as a template, synthesizes new DNA strand by adding nucleotides to an RNA primer or a pre-existing DNA strand
Q. What is sliding clamp? 위 DNA pol 3 (왼쪽) 옆 오른쪽에 붙어있는 저놈이다.
DNA polymerase 3 is closely associate with a protien called sliding clamp.
Sliding clamp is a protien that can help DNA polimerase more along the DNA template strand.
Sliding clamp can help DNA polymerase not to fall.
And can move smoothly along the strand of DNA for synthesis.
6. DNA polymerase 1 (DNA pol 1)
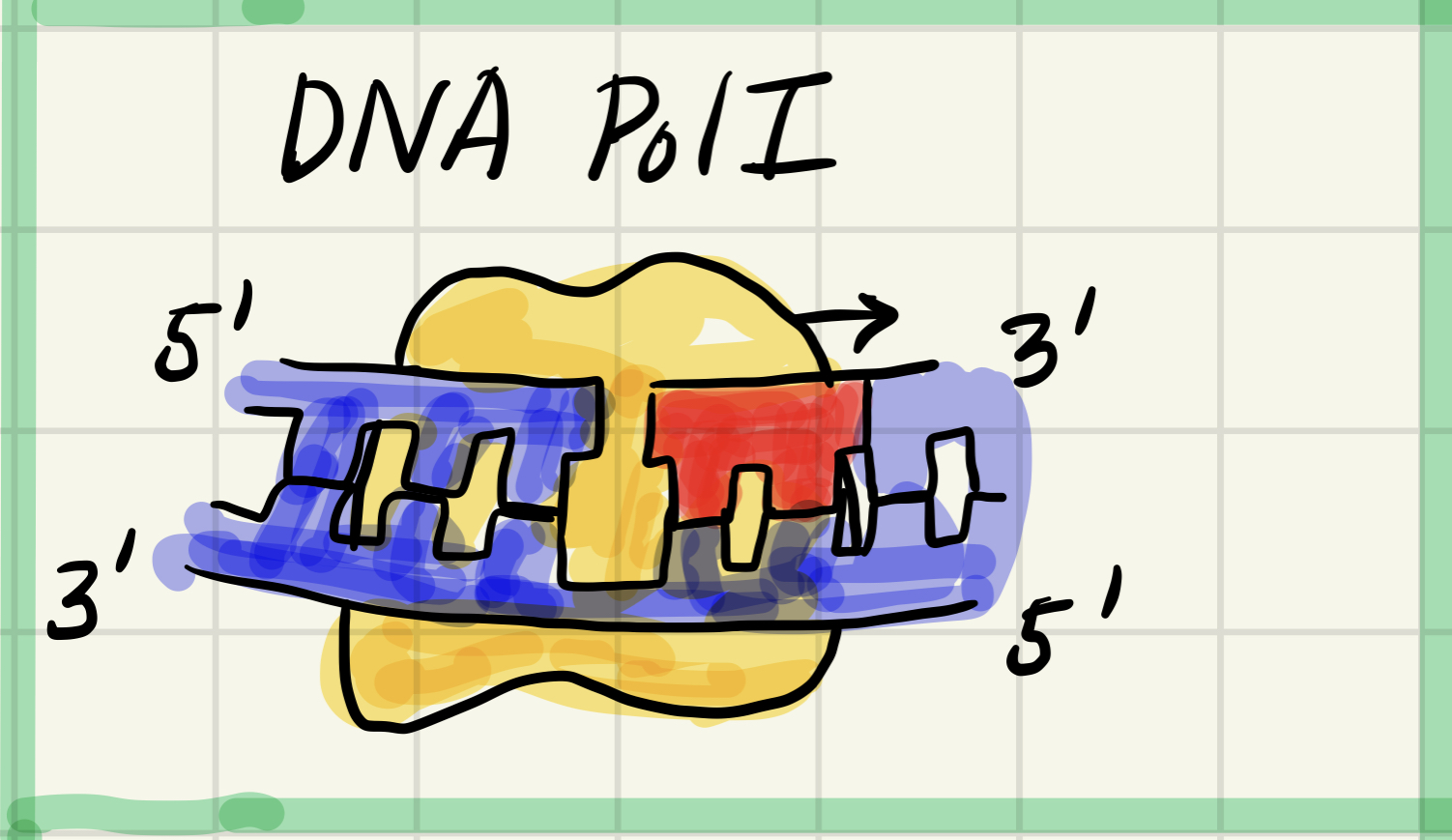
Removes RNA nucleotides of primer from 5' end and replaces them with DNA nucleotides added to 3' end of adjacent fragment
Different type of polymerase.
Replaces RNA nucleotide of the primer with DNA nucleotides.
To make the whole strand composed(구성) of the DNA nucleotide.
But DNA pol 1 can not actually join the final nucleotide of the adjacent okazaki fragment so then, need another enzyme called DNA ligase. (Joining the backbone of all okazaki fragments to amke a continuous DNA strand.)
*adjacent = neibouring
*1. DNA strand should be Anti parallel.
*2. DNA polymerase 3 can only add new DNA nucleotide in 5' to 3' direction.
7. DNA ligase
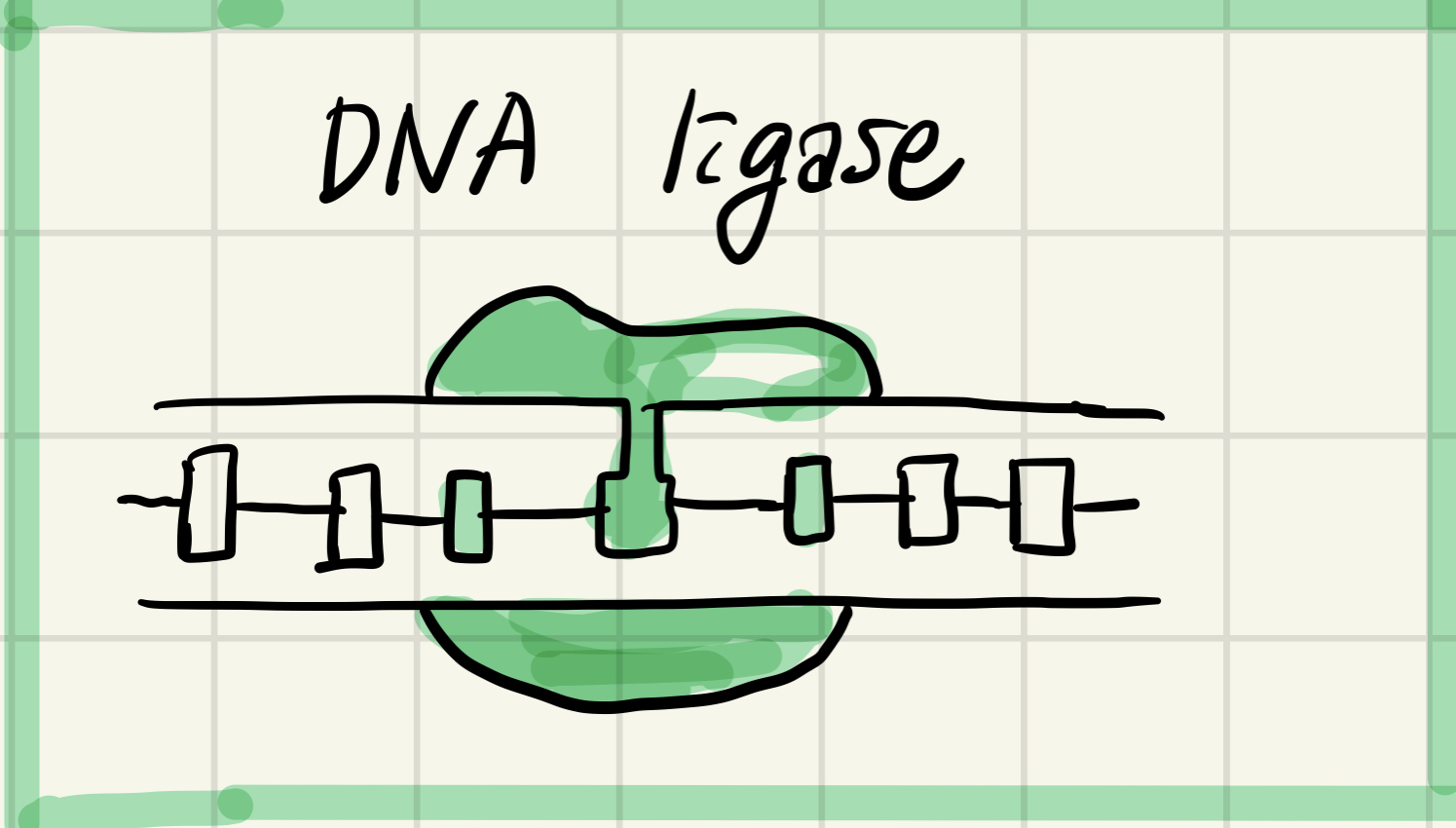
Join okazaki fragments of lagging strand; on leading strand, join 3' end of DNA that replaces primer to rest of leading strand DNA.
Joining the backbone of all okazaki fragments to amke a continuous DNA strand.
Q. Why is lagging strand named so?
Lagging strand is named so because its' synthesis is delayed slightly relative(상대적인) to the synthesis of leading strand.
*New fragments of the lagging strand cannot be started
until enough template has been exposed at the replication fork.
'BIO:logy' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 코로나 3단계 거리두기 조치 //코로나 3단계 격상 기준 (0) | 2020.12.12 |
|---|---|
| 코로나 주요 백신 화이자, 모더나, 아스트라제네카 비교 분석 (0) | 2020.12.11 |


댓글